This project is a case – study on “How you can make a Procedural Landscape in Unity3D, by using c# code”. The Landscape is produced by applying three layers of Perlin Noise on a custom mesh surface. You may edit the Landscape’s control variables in Edit Mode and get a real-time preview of the result. There is also an “animate” function which lets you explore the endless possibilities of the resulting surface.
Continue reading to learn more about the tool’s current features, future plans and see the source-code.
Current Features
Editor Preview
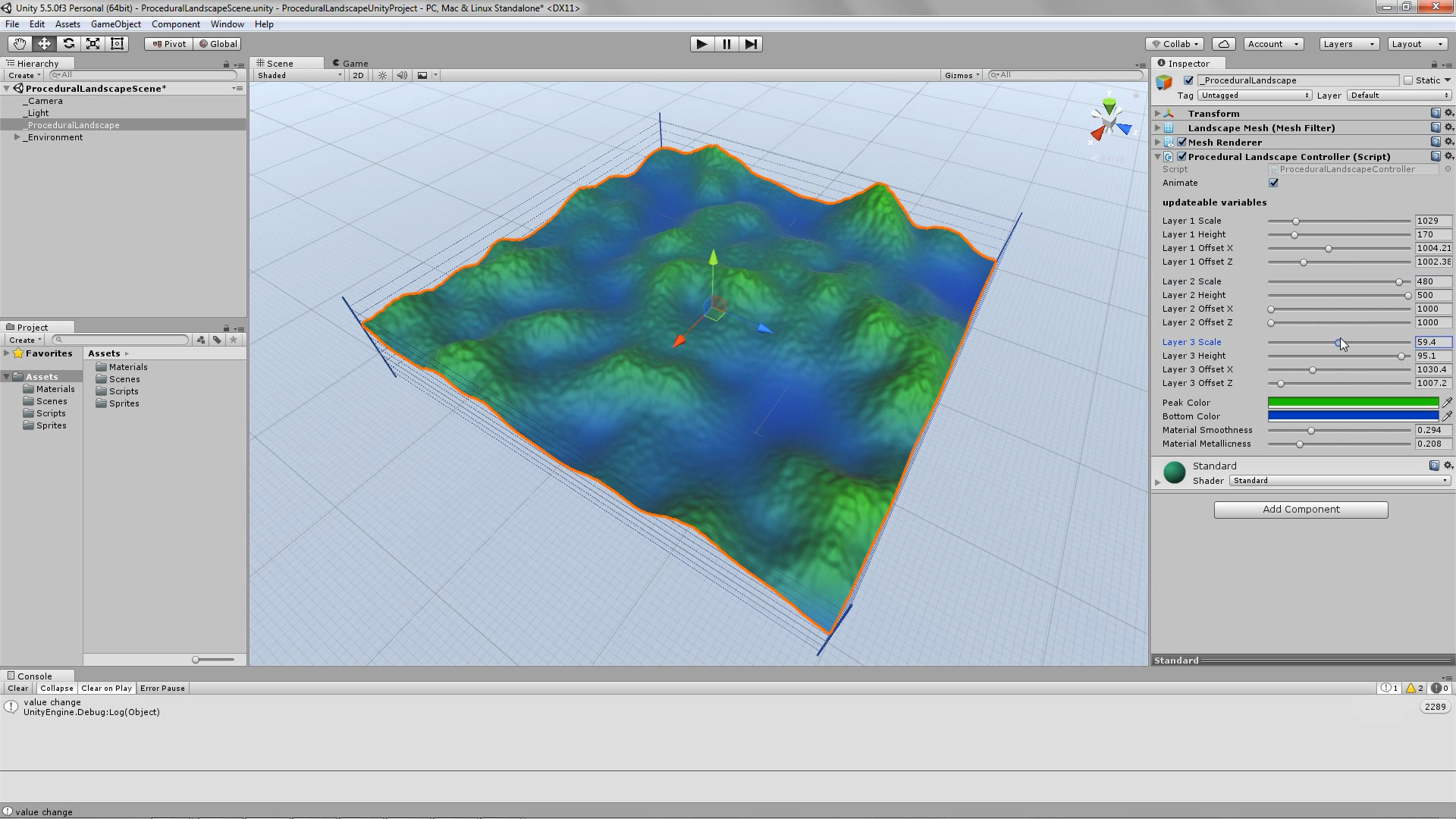
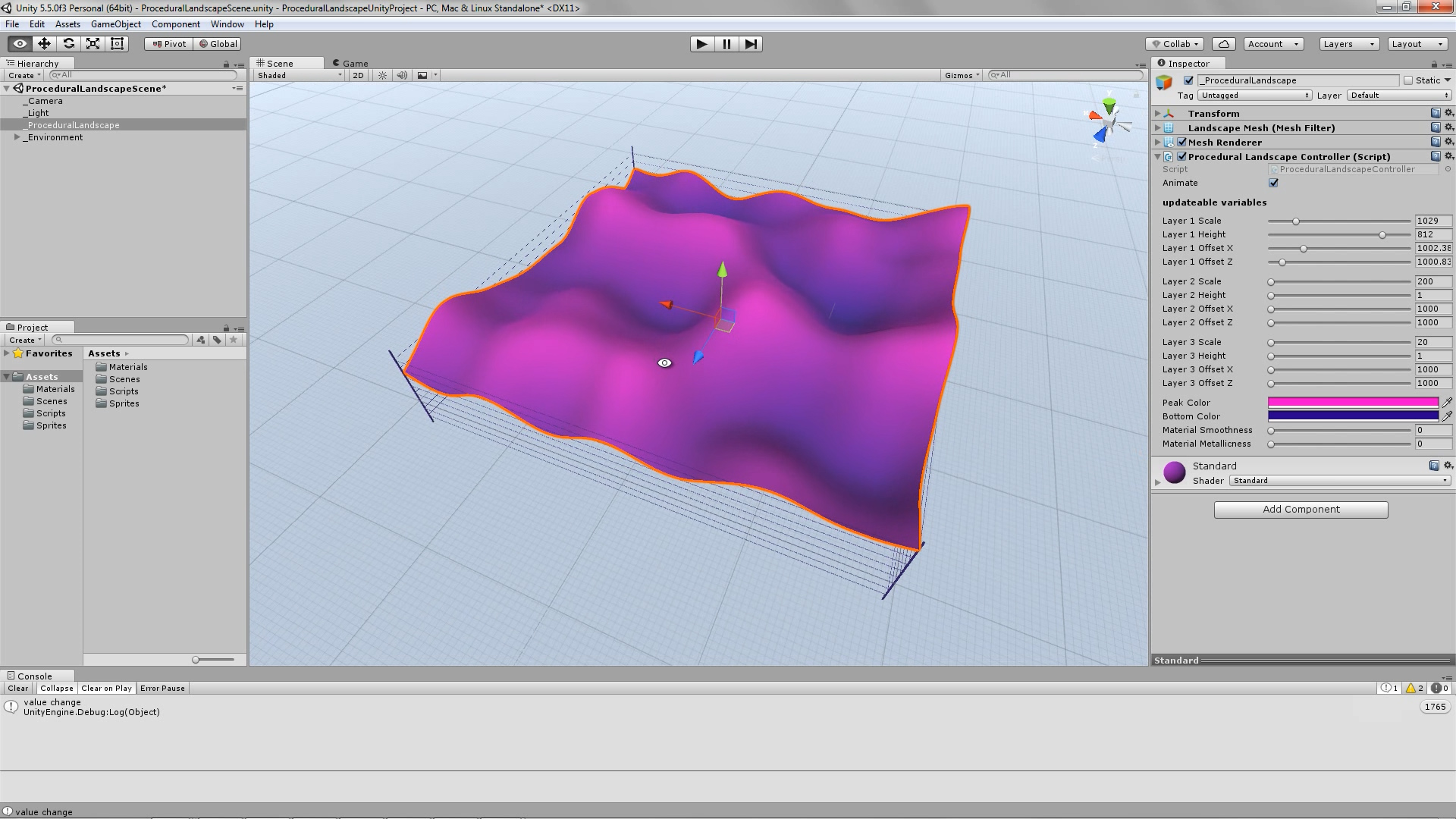
The algorithm is formed in such a way that the Landscape’s mesh is visible, even while in Edit Mode. This allows you to make changes “on the fly” and see the result in real time. If you wish to modify the Landscape’s form, simply select the “_ProceduralLandscape” object and use the sliders to modify its parameters.
The next section explains how these parameters affect the resulting geometry and appearance.
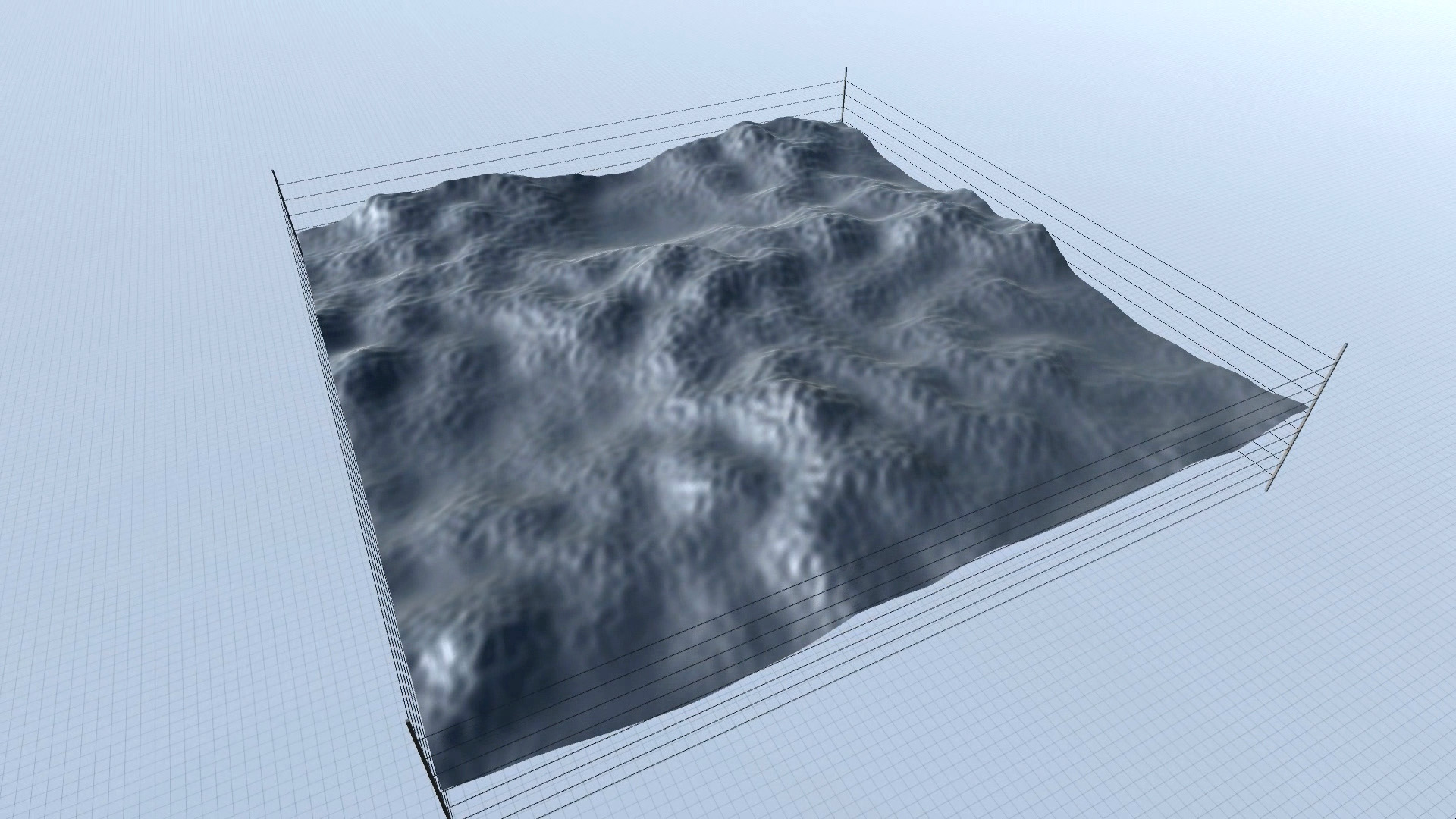
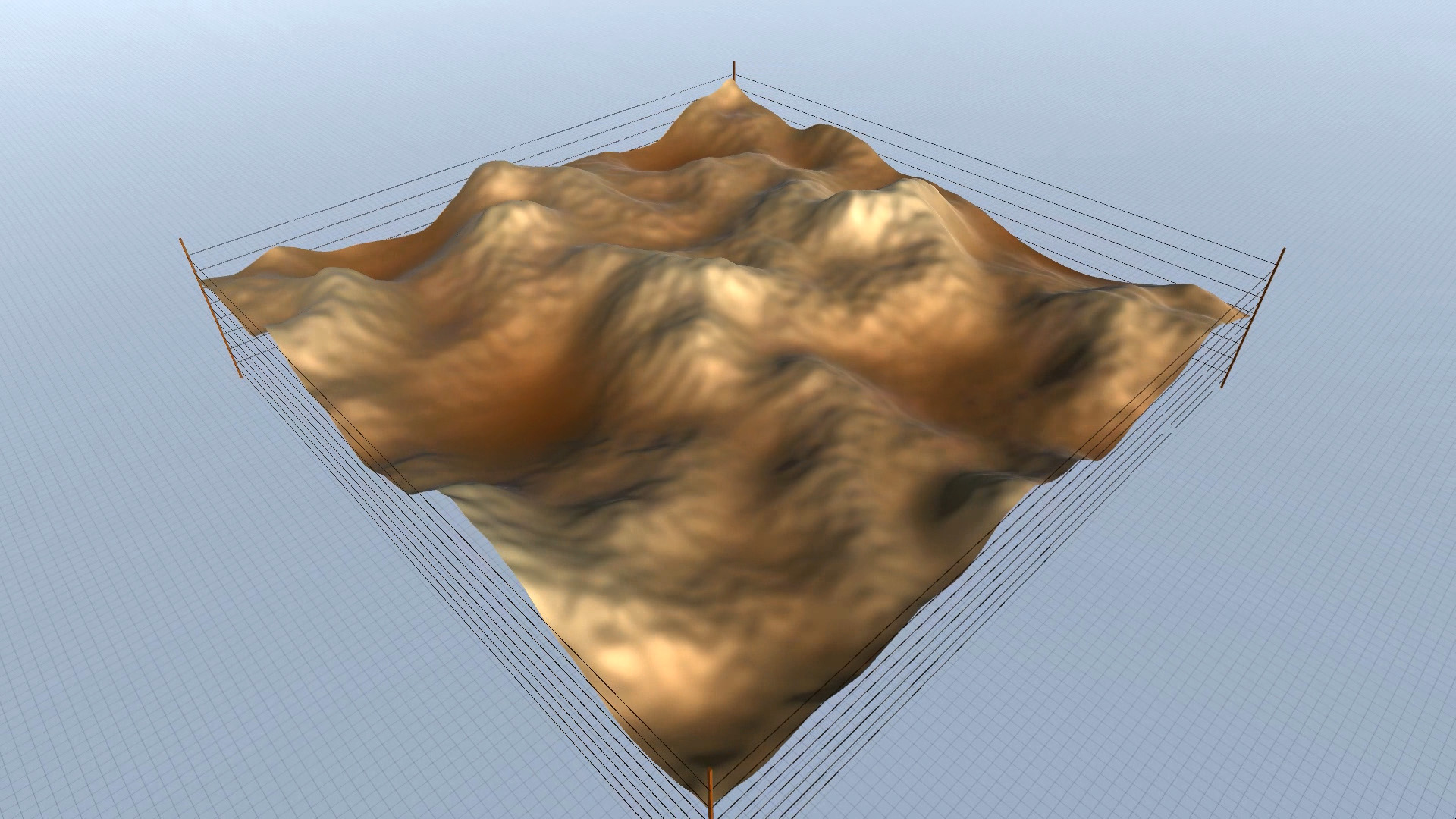
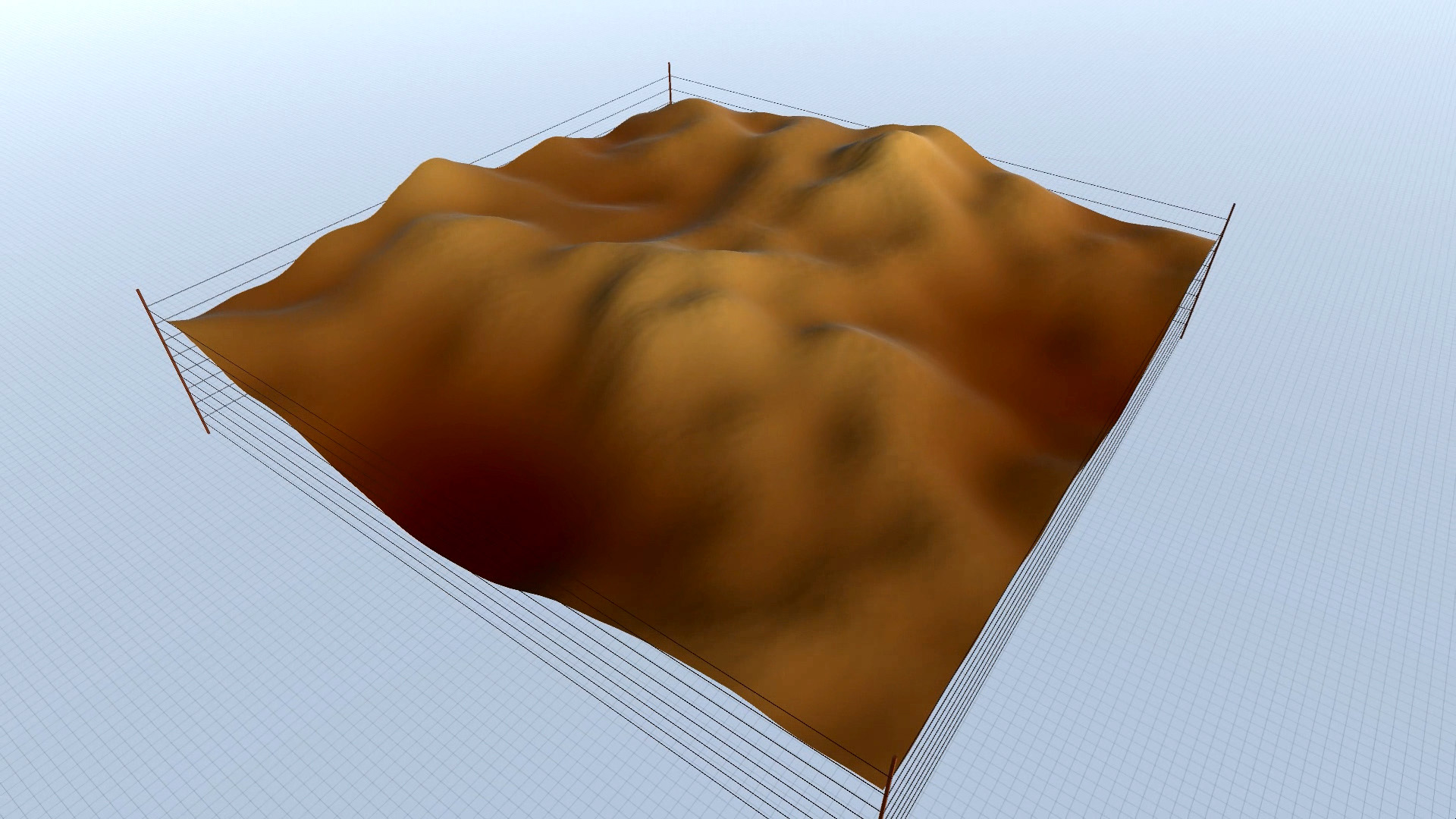
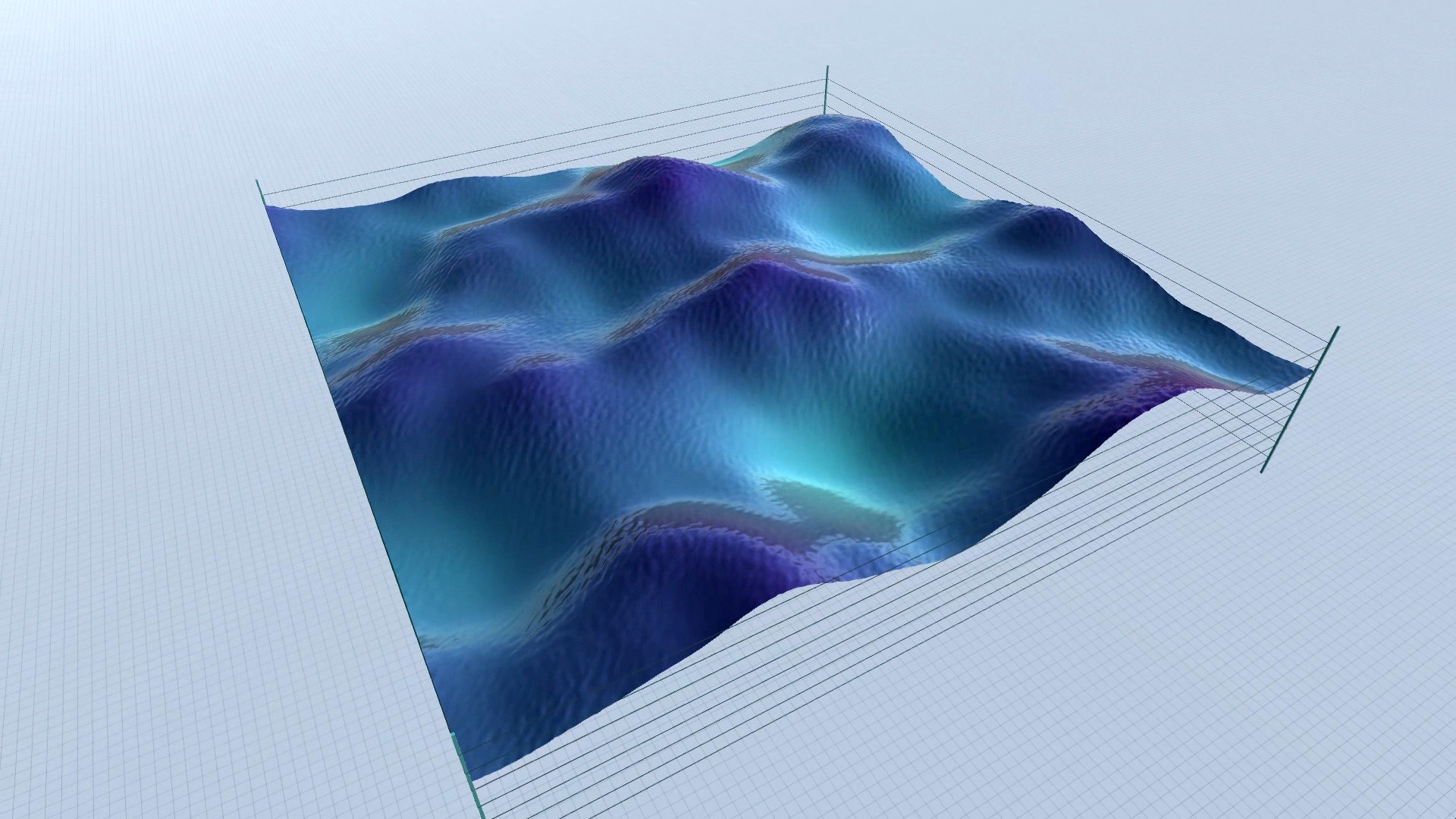
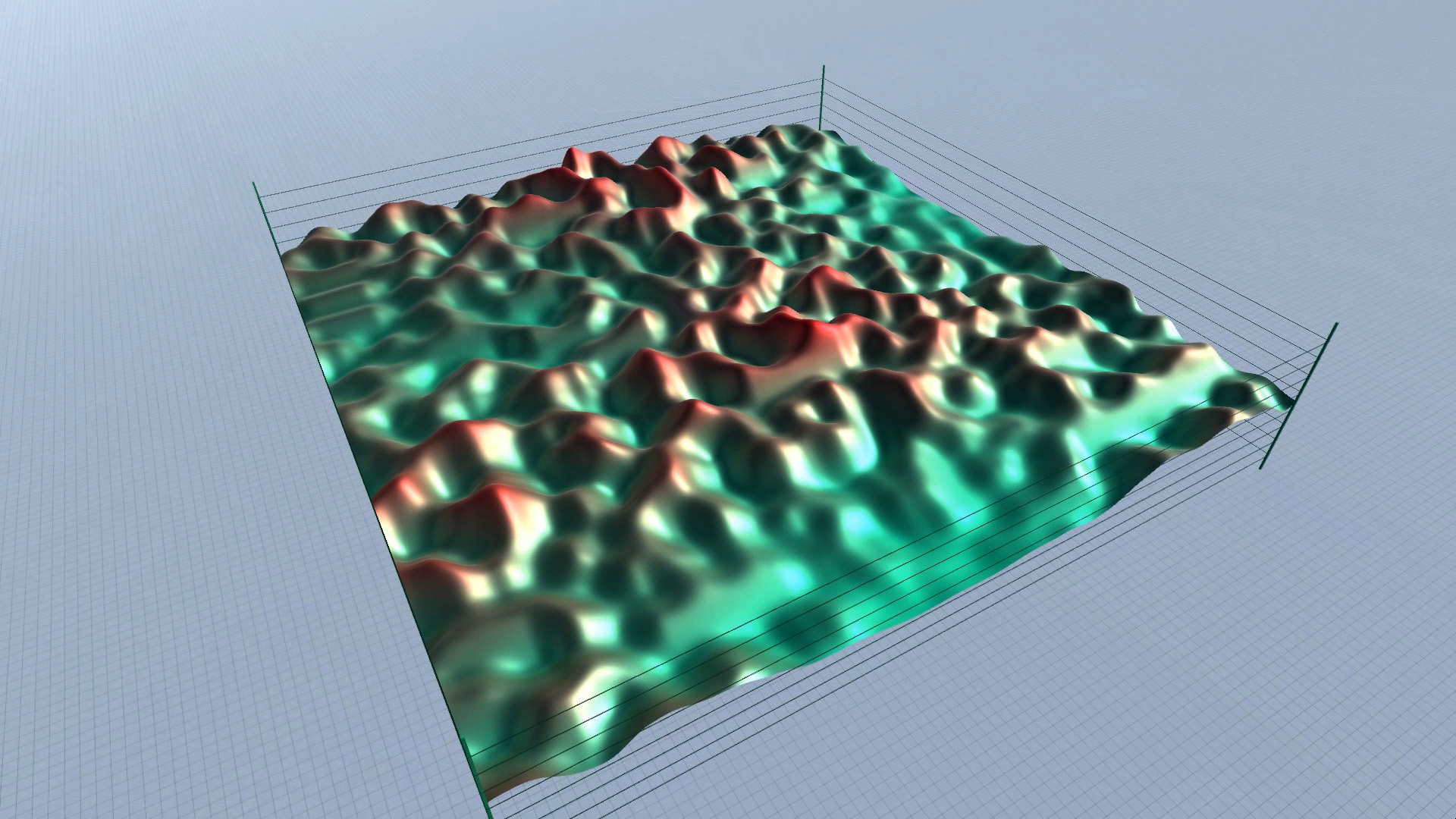
Procedural Landscape – editor screenshots – slideshow.
Editor Controls
Here lies a brief description of the available controls over the Landscape’s geometry and appearance:
Animate: This boolean parameter lets you choose whether the Landscape will be animated, while in Play Mode (read next section for more info) .
The controls for each Layer are similar (the variables are the same, but the slider-range is different).
- Layer (n) Scale: scales Layer (n) along the X and Z axes
- Layer (n) Height: scales Layer (n) along the Y axis
- Layer (n) X-offset: moves Layer (n) along the X axis
- Layer (n) Z-offset: moves Layer (n) along the Z- axis
The bottom four variables are the material’s controls
- Peak Color: sets the color of the mesh at its highest point
- Bottom Color: sets the color of the mesh at its lowest point
- Material Smoothness: sets the material’s smoothness
- Material Metallicness: sets the material’s “metallicness”
* Inorder to access the Landscape’s Editor Controls, the “_ProceduralLandscape” gameObject (the one that the “ProceduralLandscapeController” script is attached to) must be selected.
** The best way to understand how it all comes together is to test them yourself 🙂
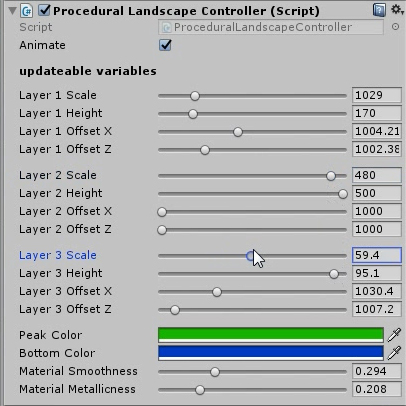
Procedural Landscape – editor – exposed variables that update the Landscape’s geometry and material.
Animated Play Mode
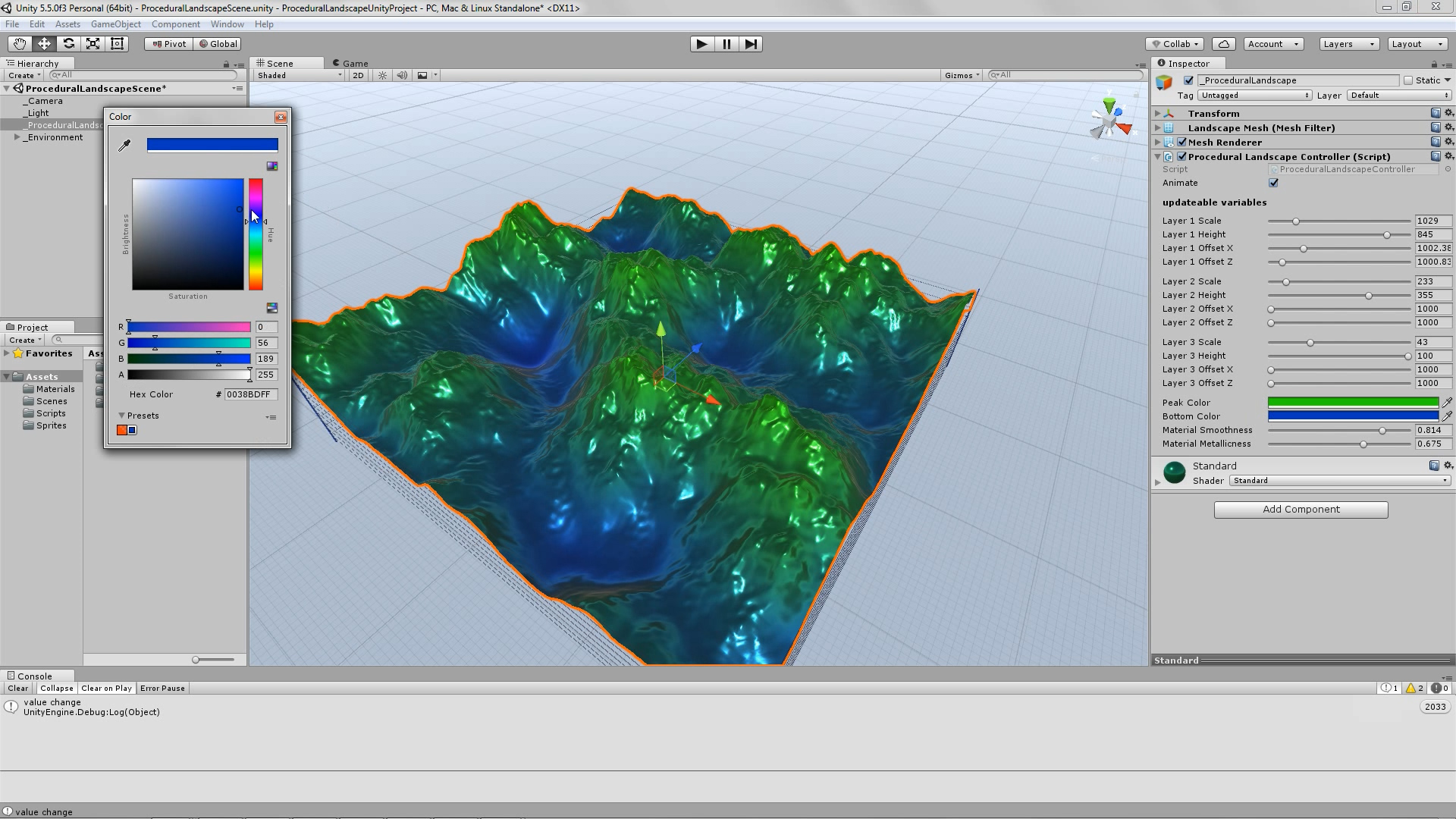
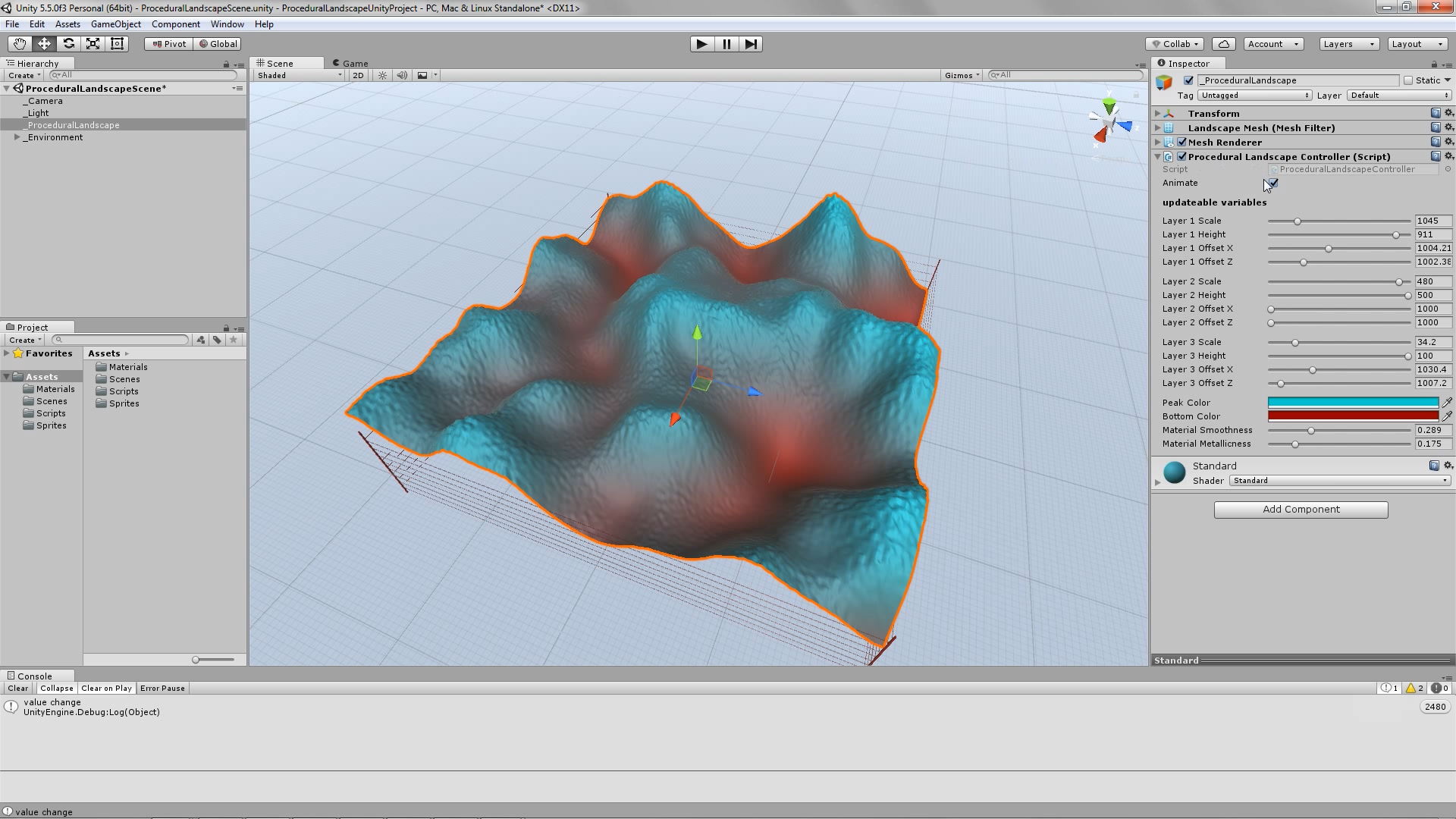
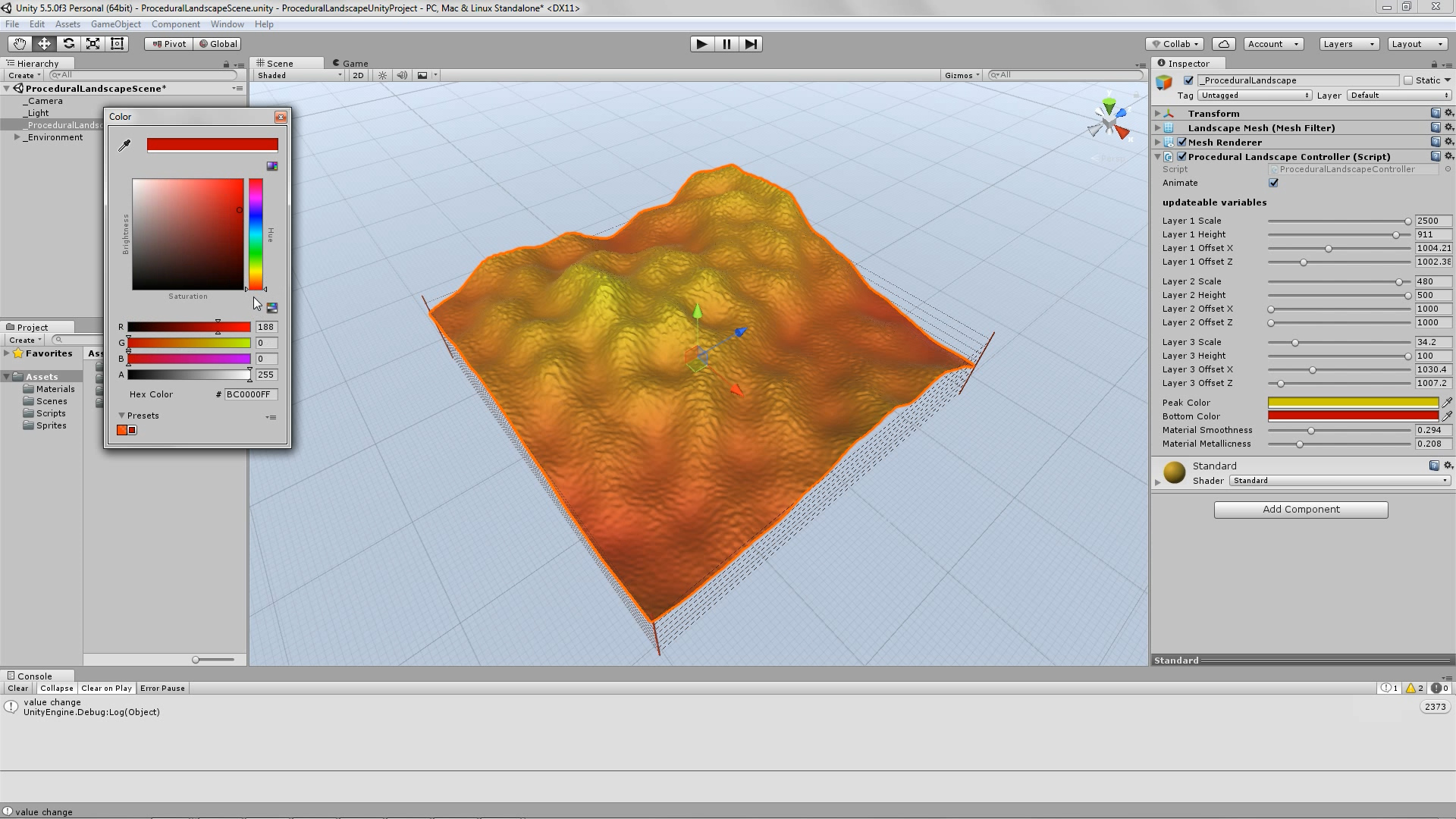
The best way to explore this script’s range of capabilities, is to use the animated play mode. In order to do that, just set the animate parameter to true (select the tick-box if it is not already selected), hit the play button, from within the Unity Editor, sit back and relax. In this case, the script takes control of its parameters, and cycles through them in a way that – mostly – avoids repetition. So you will be able to see an ever-changing landscape. And once you see something you like, just hit the pause button and write down the variables’ values, so that you can reproduce the desired result.
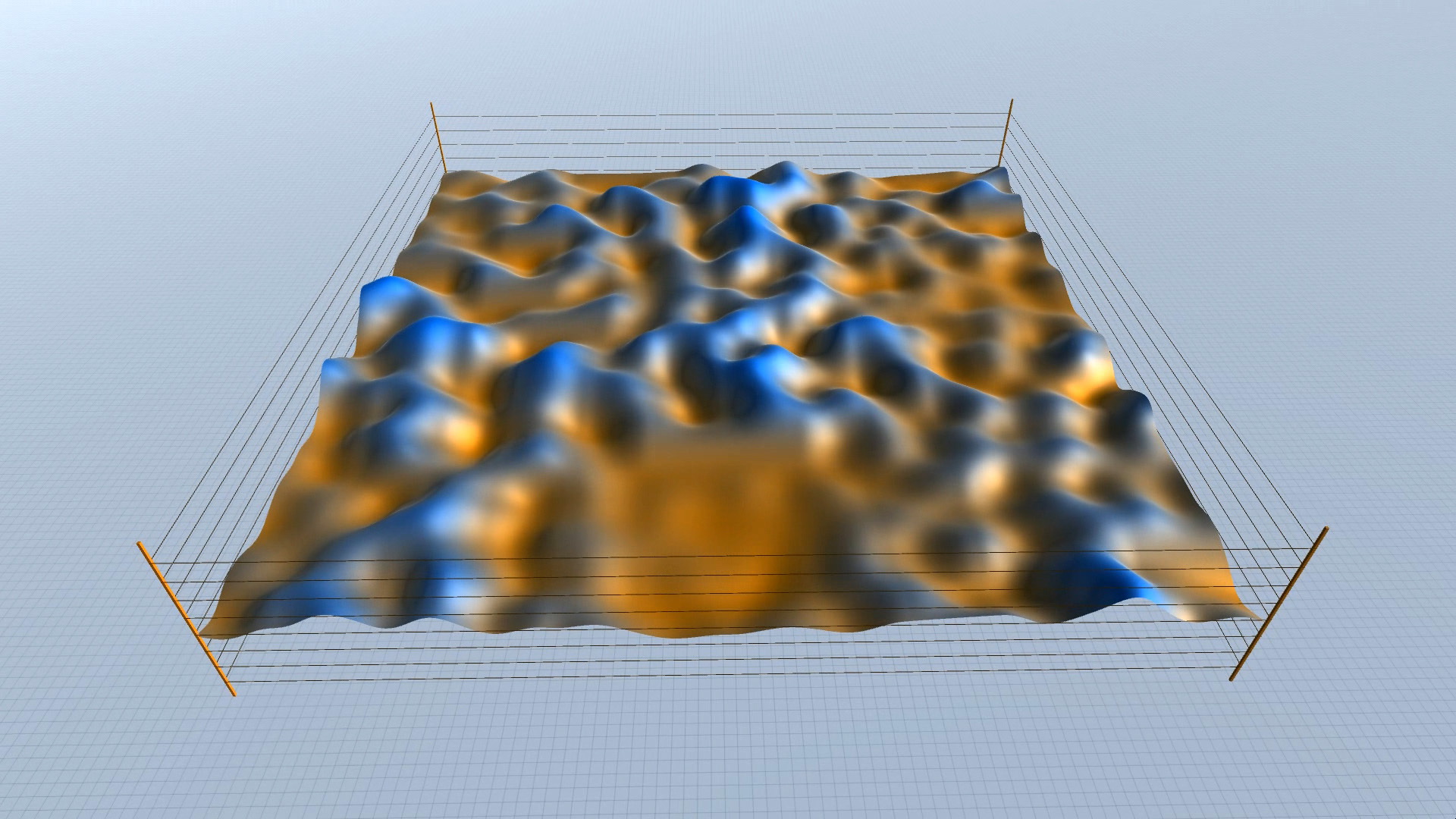
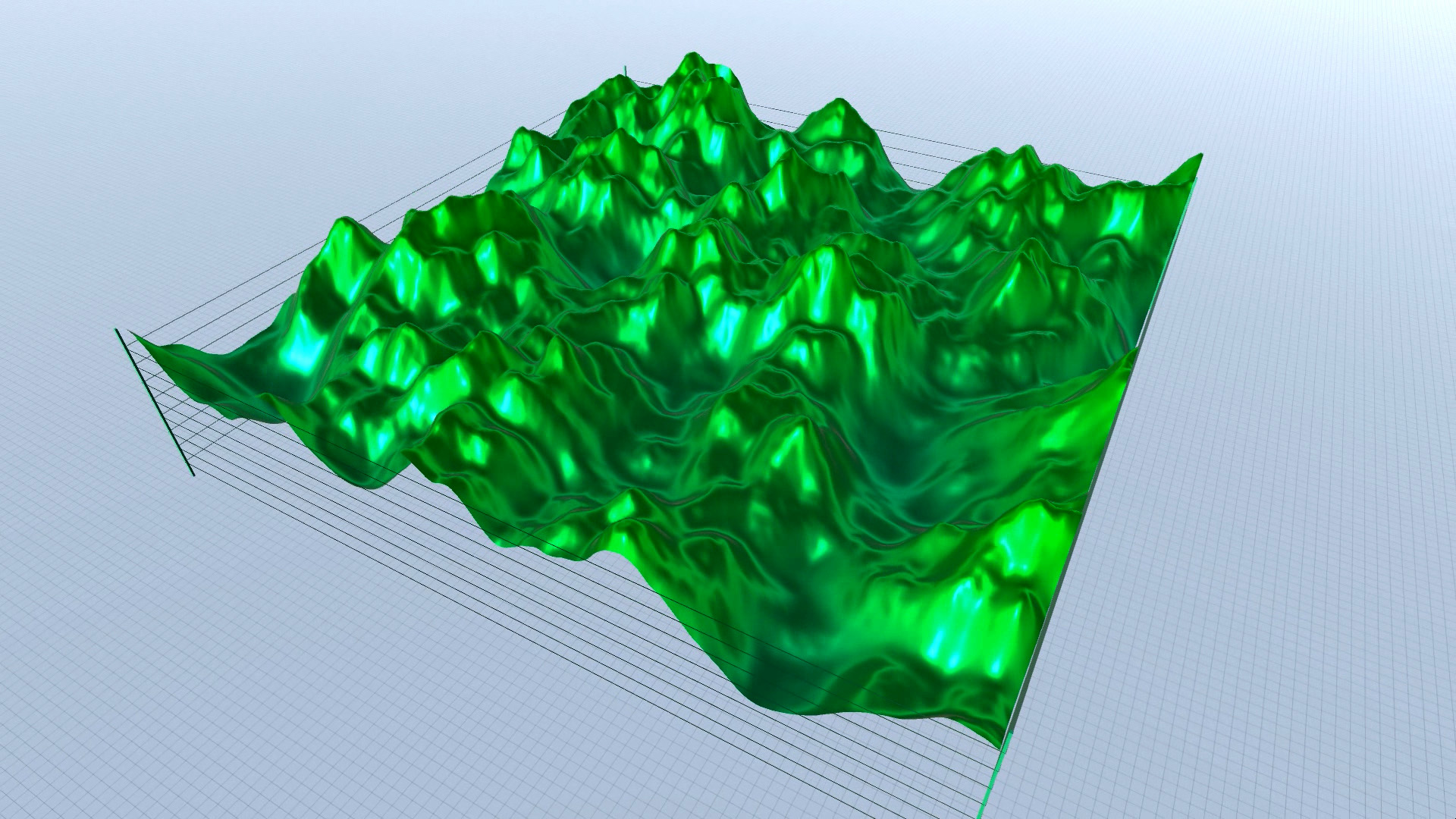
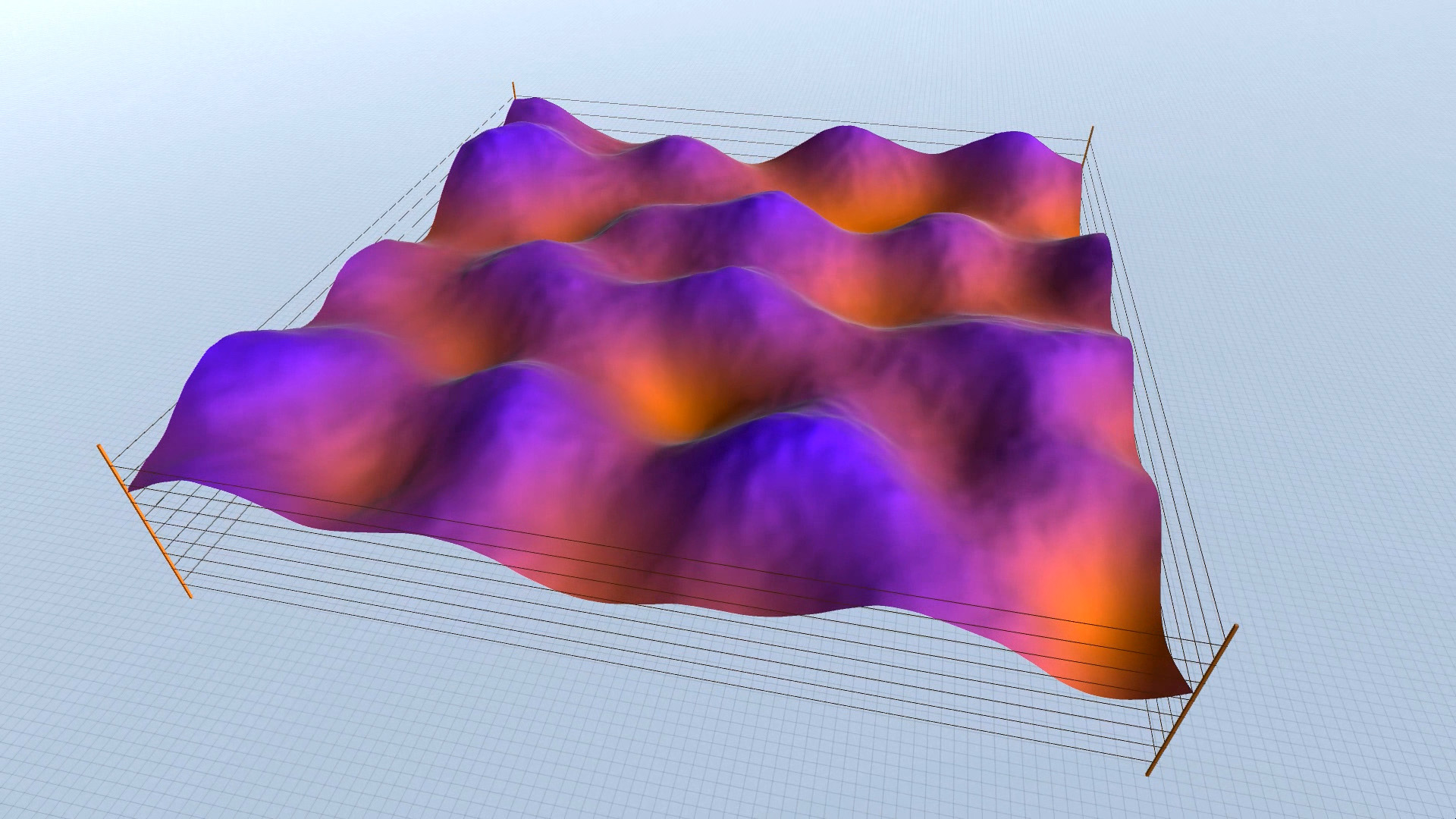
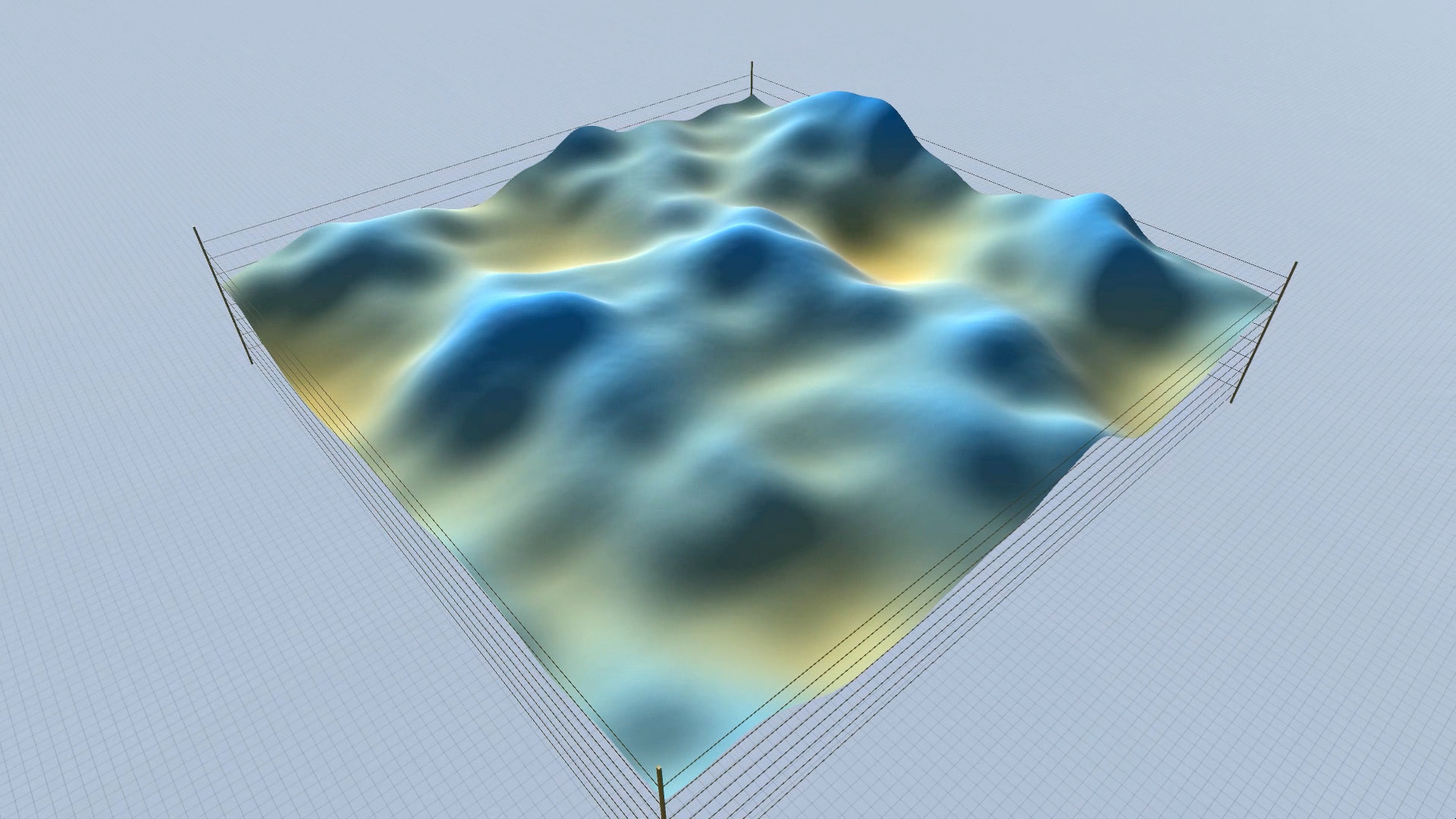
As you can see in the screenshots, some results are more realistic (resembling an actual – physical landscape), while others are more outworldly, perhaps resembling alien landscapes or other kinds of imaginary surfaces.
Procedural Landscape – animated mode – screenshots – slideshow.
Future Plans
So far, this project can be considered as a “case-study” on Landscape Generation. However, with a few extra features it could easily turn into an actual level-design tool for 3d-games. Some cool – features that I might start working on in the near future, are:
- The ability to create an actual “playable landscape” on which the player can move (actually including a mesh-collider).
- The ability to save the produced landscape into a 3d-file format (such as .dxf or .obj) for exporting into other applications.
- The ability to save the produced landscape as a prefab (So that one can create a collection of Landscape – gameObjects).
- The ability to create a never-ending world, that updates and expands itself as you explore it.
- The ability to procedurally populate the Landscape’s surface with extra – objects, such as vegetation, rock formations, etc.
One other thing that I might also get to, is the research of other techniques to produce the Landscape’s Geometry (apart from the Perlin Noise).
Source Code:
The following code is the “ProceduralLandscapeController” class. This class is a “standalone tool”, meaning that there are no dependencies to other gameObjects, prefabs, materials or other assets in the project. I took the time to fill the code with comments, so that one may easily follow the algorithm’s logic.
If you want to use the script in your own Unity Project, here are the necessary steps:
- Create a new c# script
- Name it “ProceduralLandscapeController”
- Copy – paste the code from below into your script, replacing everything else
- Attach the script to an empty gameObject, and name it “_ProceduralLandscape” (You can use any name, actually)
- Also attach a MeshFilter and a MeshRenderer component to your gameObject
Although you may copy the code (from below) into your project (and it will – most probably – work), I would suggest that you visit the “Unity3D-Coding-Examples” project on github and grab the code from the “2-Procedural-Landscape” folder. In that folder you will also find the entire Unity Project which will include the code’s latest version, as well as some extra stuff that might be useful (such as scene-objects, camera animation script etc).